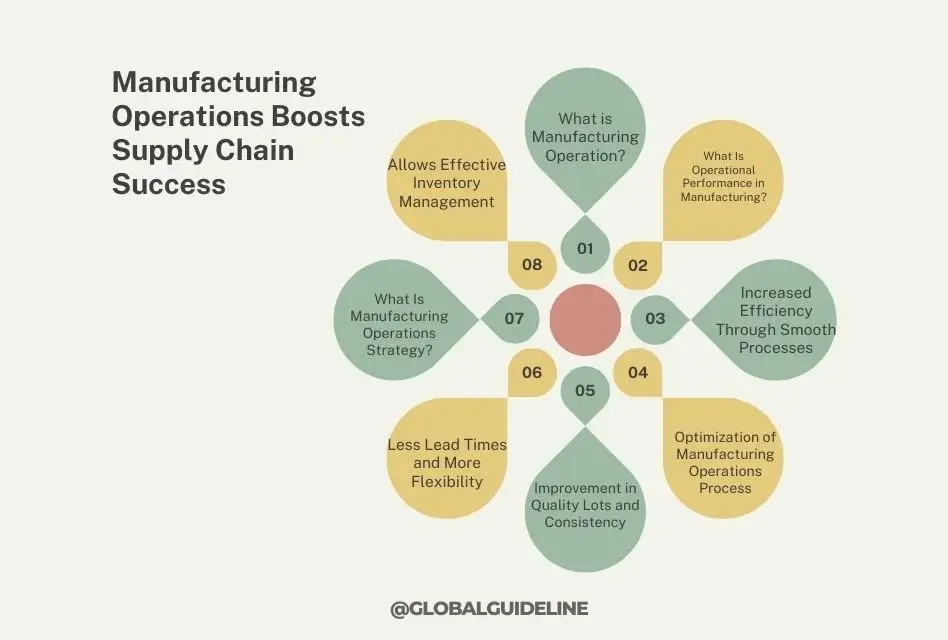
Operational efficiency and performance are keys to scaled success in today’s fiercely competitive manufacturing landscape. Indeed, effective manufacturing operations ensure better operational performance and at the same time guarantee the efficient management of the general supply chain. The article presents seven ways that manufacturing operations can help drive the success of any supply chain by illustrating key strategies, key processes, and best practices that will drive optimized results.
Table of Contents

What is Manufacturing Operation?
Before looking at the specific ways that performing manufacturing operations boosts supply chain success, it’s first necessary to understand what manufacturing operations entail. Manufacturing operation is defined as the processes of changing or altering completely or partially raw materials into finished products. The operations include activities such as production planning, inventory management, quality control in addition to actual manufacturing.
What Is Operational Performance in Manufacturing?
Operational performance in manufacturing covers the efficiency with which all these diverse processes are carried out effectively. This is measured through different kinds of KPIs that observe the efficiency of manufacturing operations with respect to attaining production goals, quality standards, and resource management. High operational performance simply means that there is a streamlined process which is highly efficient and adds some value to the supply chain.
1. Increased Efficiency Through Smooth Processes
Perhaps the most major way in which performing the manufacturing operation increases supply chain success has to do with efficiencies. Smooth manufacturing processes equate to less waste, reduced incidents of downtime, and an overall speedier production process. Lean manufacturing, for example, focuses on the elimination of non-value-added activities. The end result of this, of course, is a faster time of production along with reduced overall cost.
Example: Just-in-time inventory management is one of the most common strategies applied in lean manufacturing. Through closely aligning the production schedules with demand, companies reduce the cost of holding inventory and build responsiveness within the supply chain.
Optimization of Manufacturing Operations Process
It involves an examination of every production step for inefficiency and other better ways of performing such an operation. The companies can always refine such processes to ensure that operations also contribute to making the supply chain more agile and responsive.
2. Improvement in Quality Lots and Consistency
Manufacturing operations are also crucial to the success of the supply chain betterment in the quality and consistency of the products. High-quality products reduce the possibility of returns and recalls, dissatisfaction of customers that disrupts the supply chain.
Key Performance Indicators for Manufacturing Operations Management
It oversees the indications of key performance for the quality of the product by taking into consideration the defect rates or customer complaints, thus allowing the manufacturing operation to remain within the circle of high standards. Such indicators can serve to identify, at an early stage, many of the problems arising during production and enabling corrective actions before defective products reach the customer.
Example: A company may track the percentage of products first-pass quality control inspection to evaluate manufacturing operational performance. Consistently higher rates lower risk within the supply chain.
3. Less Lead Times and More Flexibility
Carrying out manufacturing operations effectively assists in reduction of lead times, enhancing flexibility. Responding speedily to changes in demand in a fast-moving market is a considerable competitive advantage.
What Is Manufacturing Operations Strategy?
A properly focused manufacturing operations strategy will reduce lead times by optimizing production schedules, improving workflow, and adopting flexible manufacturing systems. The immediate solution would be proper strategy on manufacturing operations, which essentially would reduce the lead times through optimizing the production schedule, enhancing the workflow, and making use of flexible manufacturing systems. This will be important in responding to customer demand and keeping the supply chain fluent.
Example: For instance, when adopting modular production, a manufacturer could switch lines of production with ease and speed; this would reduce time taken for the delivery of new orders and allow them to adapt to market changes in a far timelier manner.
4. Allows Effective Inventory Management
Inventory management is an essential part of supply chain success. Manufacturing operations play a significant role in the area of effective management of inventories. Simply stated, effective inventory management ensures availability of raw materials and finished products as needed with neither overstocking nor understocking.
Manufacturing Operations versus Service Operations
Unlike service operations, which basically deal with intangible outputs, manufacturing operations deal with physical goods. This implies that inventory management in manufacturing has to grapple with storage, handling, and movement both of raw materials, work-in-progress, as well as finished products.
Lean Manufacturing Operational Performance
Operational performance is inlaid, or rather interlinked, with inventory management practices in lean manufacturing. Techniques like Kanban systems help in regulating the material flow for keeping inventories at levels that can meet production needs without excess.
Example: A company using a Kanban system may be able to reduce its inventory level by 20%, with resultant lower carrying costs and a more responsive supply chain.
5. Facilitates Collaboration Across the Supply Chain
Efficient manufacturing operations also cultivate cooperation along the supply chain. It can be effected by instituting appropriate and transparent channels of communication between suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors. This cooperation will facilitate coordination of activities, sharing of information, and ensure that all parts within the supply chain pull in the same direction.
Manufacturing Operations Examples
Examples of this collaborative effort in manufacturing operations include joint product development initiatives, shared forecasting, and synchronized production schedules. This can help in aligning the whole supply chain, thereby minimizing the chances of any bottleneck and increasing the performance of the entire supply chain as a whole.
Example: A close collaboration of a manufacturer with one of its key suppliers on the development of a new material can lead to cost savings and better product performance, eventually benefiting the companies and the supply chain.
6. Enhancing Responsiveness to Market Demands
Responsiveness is the key to success in the dynamic market conditions today. The manufacturing operation in agile and flexible manners assists firms to respond in the shortest time to changes in customer demand, market conditions, or disruptions in the supply chain.
How to Manage Manufacturing Operations?
The management of manufacturing operations for improving responsiveness takes into consideration flexible production systems, cross-training employees, and investment in technologies that are built to handle rapid changes in production schedules.
Example: It enables a firm to respond to new emerging market trends in rapid prototyping, followed by production of new products with the help of advanced manufacturing technologies like 3D printing or computer-assisted design, thus keeping the supply chain agile and competitive.
7. Improved Sustainability and Reduced Environmental Impact
Increasingly, there is a consideration of sustainability with regard to supply chain management. Manufacturing operations that take into consideration environmental impact go a long way toward supply chain success. In fact, sustainable manufacturing practices minimize waste, reduce energy consumption, and decrease reliance on hazardous materials.
Manufacturing Operations Management and Sustainability
The management of manufacturing operations itself implements sustainable operations, such as energy-efficient production processes, recycling programs, and renewable materials. In this manner, it lessens the footprint of a company on the environment and boosts its reputation along with improved regulatory compliance.
Example: A firm can replace the traditional manufacturing system by adopting a closed-loop manufacturing system whereby waste materials are recycled back in the production process to reduce the cost of disposing of waste while improving sustainability metrics in support of greener supply chains.
Various Job Positions in Manufacturing Operations
Identifying the various roles within manufacturing operations is important to anyone who would wish to seek a career within this field. These range from entry-level positions to management, each being important in manufacturing processes and the supply chain as a whole.
Manufacturing Operations Job Description
The general description for the manufacturing operations job would involve being responsible for the production process, teams, and quality control, besides the optimization of workflow. In the course, a close look into manufacturing technologies, methodologies for process improvement, and supply chain management is required.
Performing Manufacturing Operations Jobs
Jobs related to performing manufacturing operations may include hands-on work with machinery, supervision of production lines, or strategic planning targeted at enhancing the efficiency of the operations. These are crucial jobs that ensure smooth manufacturing operations add value to the supply chain.
Example: A manufacturing operations manager may be tasked with the responsibility of implementing lean manufacturing techniques for various production lines, yielding cost savings along with improvements in product quality.
The Importance of Training and Certifications
Training and certification are very important to enhance continuously the competence of production staff in their knowledge and qualifications to ensure optimal operational performance. Courses such as the City and Guilds Process Technology Level 3 or an NVQ in Performing Manufacturing Operations provide the individual with the basic knowledge and expertise for this type of work.
City and Guilds Process Technology Level 3
This certificate focuses on advanced manufacturing processes, quality control, and operational efficiency. It is also targeted at individuals who wish to enhance their understanding of process technology and expand job opportunities for themselves in manufacturing operations.
Manufacturing Operations NVQ
The NVQ in Performing Manufacturing Operations is a competency-based qualification that has been designed to confirm the competence of a candidate in performing tasks within manufacturing. This will be useful to anyone desiring to demonstrate their competence and enhance their career prospects in manufacturing.
Example: Those employees who gain this NVQ in Performing Manufacturing Operation may be better positioned for promotion or more complicated roles inside their organizations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Operational Performance in Manufacturing?
Operational performance refers to the effectiveness and efficiency of the manufacturing process. It is defined by key indicators like rates of production, levels of quality, and resources utilized.
What are Manufacturing Operations?
Manufacturing operations are about production planning, inventory management, and quality control in the process of manufacturing goods from raw materials.
How to manage manufacturing operations?
Manufacturing operations management involves the optimization of production processes, putting in place quality control measures, and ensuring measures that facilitate efficiency in resource utilization. Effective management thus leads to improved operational performance and success of the supply chain.
What Is the Manufacturing Operations Strategy?
A manufacturing operations strategy is a way a firm does things in managing and controlling its production process, and it typically covers a number of dimensions related to efficiency, flexibility, quality, and sustainability.
What Are the 7 Steps of Manufacturing?
In general, they include design, material selection, production planning, fabrication, assembly, quality control, and distribution of the seven manufacturing steps. Each one of them is vital in one way or another to ensuring the successfulness of the manufacturing process.
What Are the Functions of Manufacturing Operations?
Manufacturing operations mainly consisted of production planning, inventory management, quality control, and optimization of the process. These functions ensure high-quality products are delivered on schedule and within budget.
What is the difference between manufacturing and service operations?
Manufacturing operations deal with the production of tangible goods, while in service operations, the area of concern is intangible services. While both need efficiency in processes and their management, they differ in output and resource management perspectives.

What are some examples of manufacturing operations?
Examples of manufacturing operations include assembly lines, batch production processes, and continuous flow production. Each one shows a different way of organizing and carrying out the manufacturing job.