The management in modern times by a Chief Scientific Officer or CSO has become very significant in driving the forces of innovation that provide a differential advantage in industries, especially in biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, and research institutions. A Chief Scientific Officer manages the scientific research and development activities in any organization to align them with the strategic direction which the company should take for its growth and success.
Below is a review of the top 5 responsibilities of a Chief Scientific Officer in the USA, giving great insight into what this executive role entails and how it partners in driving organizational success.
Table of Contents

1. Strategic Leadership in Research and Development
What Does a Chief Scientific Officer Do?
The Chief Scientific Officer at the heart of it manages research and development work in institutions on strategic levels. The CSO plays a key role in defining the scientific course the company will take, keeping research activities in line with the goals of the company in the long run.
Key Responsibilities:
- Setting the Scientific Agenda: The CSO works in close coordination with other senior officers, such as the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Technology Officer, to establish an all-inclusive R&D strategy that coincides with the company’s mission and vision.
- Prioritizing Research Projects: The CSO has to conceptualize and prioritize those research projects that can bring about radical improvement or commercial gain. He needs to decide on the allocation of resources and project timelines.
- Encouraging innovation: The CSO will encourage an innovative culture in the R&D department. This includes keeping abreast of the latest scientific breakthroughs and technologies and then applying them to the company’s research work.
What Does a CSO Do in a Biotech Company?
That’s a keener responsibility in biotechnology firms, where the CSO oversees emerging technologies and products that may have widespread implications for health and medicine. The CSO must balance ensuring that all research activities meet regulatory standards and ethical guidelines while pushing the envelope of what’s possible in biotech innovation.
2. Management and Leadership of Scientific Teams
Chief Scientific Officer Job Description: Leadership and Management
The management and leading of scientific teams that will form part of the organization are a big part of the CSO’s role. This includes heading a group of researchers, scientists, and technical staff in a way that they are productive and effective towards the scientific goals of the organization.
Key Responsibilities:
- Team Leadership: This involves guidance and mentorship to the scientific team by the CSO, hence creating an environment that is collaborative and innovative. In fact, this leadership aspect is highly essential to keep productivity and the level of creativity at a high level.
- Recruitment and Development: The CSO is sometimes tasked with the recruitment of top scientific talent. They also lead in professional development through ensuring that team members have all the necessary resources and training to excel in their role.
- Performance Appraisal: Besides the above responsibilities, assessment of the performance of the scientific staff on a regular basis is also a vital responsibility. The CSO has to ensure that each and every member is achieving his or her objectives and thereby working toward the overall successful outcome of the R&D projects.
What Is the Difference Between COO and Chief Scientific Officer?
While the roles of both the COO and the Chief Scientific Officer have to do with leadership, there is a wide variation in their responsibilities. The COO is mainly into the daily management of the company to ensure that all sections within the organization work well and that the job is well executed. The CSO has to do with scientific research and development of the company, hence setting a push for innovation at the scientific perspectives of the company.
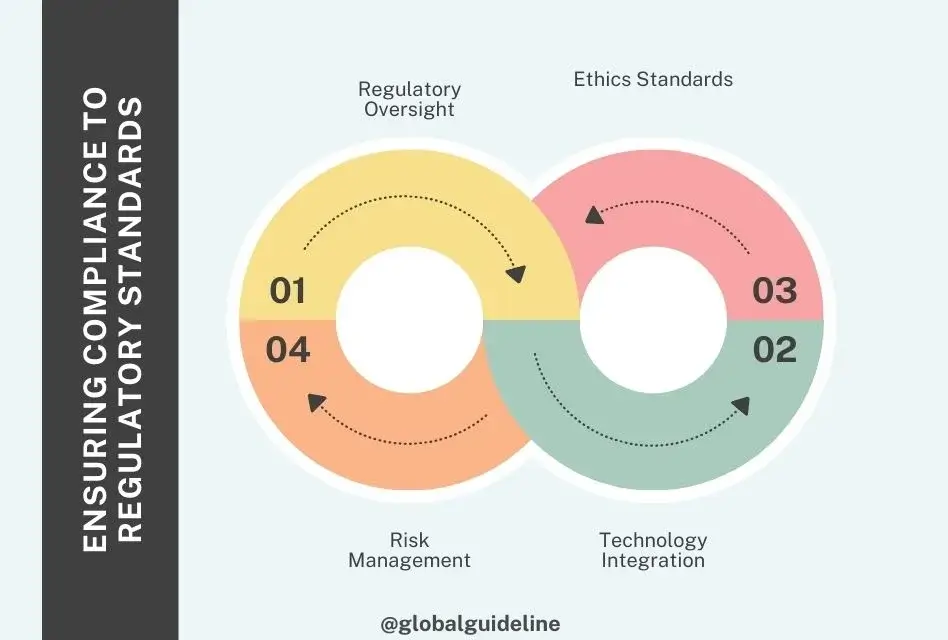
3. Ensuring Compliance to Regulatory Standards
Chief Scientific Officer Regulatory Compliance
Due to the nature of this role, particularly in fields such as biotechnology and pharmaceuticals, where the research often goes into areas considered sensitive by very strict regulatory environments, the assurance of compliance with legislation, regulations, and ethical standards in general would fall squarely as a key role of the CSO.
Key Responsibilities:
- Regulatory Oversight: The CSO will have the responsibility for assuring all research activities using animals are performed with regard for the laws, regulations, and policies of the State of California, United States federal government, and relevant international oversight authorities. This would include adherence to US FDA guidelines for research in compliance with GLP and/or GCP standards.
- Ethics Standards: It is also the responsibility of the CSO to uphold the highest ethics in research. That is, carrying out experiments and studies with integrity, transparency, and respect for human and animal rights.
- Risk Management: The significant responsibility also pertains to the identification and mitigation of risk in research activities. The CSO has to make sure that any potential risk is assessed and appropriate measures laid down to manage such risk.
Chief Science Officer vs. Chief Scientific Officer: Differences and Similarities
While the titles sound similar, the roles of Chief Science Officer and Chief Scientific Officer can be very different and depend on the company. At some companies, for instance, the Chief Science Officer may be more focused on bringing scientific knowledge to bear on solving business issues, while the Chief Scientific Officer has more critical involvement in research and development work. In practice, though, the responsibilities often do overlap, especially in areas related to ensuring regulatory compliance and ethical standards in scientific research.
4. Leading Innovation and Technological Advancements
Role of the Chief Scientific Officer
A major part of the job of a CSO involves leading innovation and technological change within a company. This encompasses staying updated on emerging scientific discoveries and ensuring the participating company seizes the opportunities in these areas for their competitive advantage.
Responsibilities Include:
- Technology Integration: The CSO is responsible for identifying new technologies that can help the firm in its research or product development. This could be in the form of new laboratory techniques, the latest equipment, or perhaps new scientific methodologies.
- Collaborations and Partnerships: Accordingly, the CSO might also seek an alliance with universities, research institutions, or other firms to realize innovations. The partnership can offer novel ideas, technologies, or resources that will speed up the company’s R&D efforts.
- Management of Intellectual Property: A very critical responsibility is protecting the innovations of the company through patents and other forms of intellectual property protection. The CSO will liaise with the legal teams to ensure that all innovations are best protected.
What Is the Difference Between CTO and Chief Science Officer?
Worth noting is that, generally, the CTO oversees the technological infrastructure and IT strategies, while the CSO concerns himself with scientific research and development. Though both roles are drivers of innovation, the concern for technology and systems remains with the CTO, while scientific advancement in application to product development and research falls under the ambit of the CSO.
5. Reporting and Communication with Stakeholders
Chief Scientific Officer Job Description: Reporting and Communication
A CSO is to report on the status and progress of research and development work within the company, including but not limited to the board of directors, investors, and other senior members of the management.
Responsibilities:
- Regular Reporting: The CSO will be involved in writing full reports on the various stages that the different research projects may have attained. This entails critical milestones reached, various challenges faced, and key successes. These reports are useful in communicating with stakeholders and making decisions.
- Presentations to the Board: In many cases, the CSO is assigned the task of presenting scientific strategies and development to the board of directors. This therefore, entails taking hard scientific concepts and interpreting them to those who may not understand it as well.
- Investor Relations: If the company is publicly listed, or a startup intending to raise capital, the CSO may be involved in investor relations, therefore demoing a showcase of the potential of scientific research at his or her company and how they fit into the overall business strategy.
Which One Has Greater Authority: CEO or CTO?
In the corporate hierarchy, the CEO is the topmost in the organization, where one would expect to take final responsibility for the company’s success. The CTO and CSO, along with the rest of the C-level officers, report to them, making the CEO the most powerful. Each has his domain of influence, where the expertise of the CSO becomes critical for steering the scientific course.

Common Job Interview Questions: Chief Scientific Officer
How to Prepare for a CSO Role
If you aspire to be a Chief Scientific Officer, you may expect various kinds of Chief Scientific Officer Interview that will assess your strategic vision, leadership qualities, and knowledge of the industry. A few of the common Associate Scientific Director Job Interview Questions for the post that are likely to be asked are given below:
- What do you think is the best way to define the scientific strategy of a company?
Describe how one prioritizes a research and development process in line with the company’s overall objectives. How does one eliminate projects to retain only those with high potential for innovation and impact? - How would you ensure your team conducts activities in research by adhering to regulatory and ethical standards?
Describe strategies for ensuring this compliance with relevant regulatory bodies and the observance of ethical standards across all research activities. - Can you give an example of how you have driven innovation in your previous role?
Share specific examples of when you identified new technologies or methodologies that significantly advanced the company’s research capabilities. - How do you explain complicated scientific topics to nonscientific stakeholders?
Emphasize that you will simplify the technical information and present it so that this information would be understandable and useful for all.
Success Tips
- Demonstrate Leadership: Evidence to having led diverse scientific teams and driven the company’s research agenda.
- Show Innovation: Provide examples from your past job about how you encouraged innovation and technological advancement.
- Data-Driven: Strategy and decisions to be discussed during the interview should be supported by data and real examples.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the responsibilities of a Chief Scientific Officer?
The CSO is responsible for research and development, setting priorities in the scientific agenda, management of scientific teams, monitoring regulatory aspects, driving innovation, and communication with stakeholders.
How much salary does a Chief Scientific Officer earn?
In the USA, the salary range of a Chief Scientific Officer greatly varies, depending on the industry to which the company belongs, its size, and location. Generally, however, the average chief scientific officer salary falls within a bracket from $150,000 to over $300,000 annually, including those from the biotech sector who most of the time get higher salaries.
How to become a Chief Scientific Officer?
Some of the broad pre-requirements for a Chief Scientific Officer will be a generalist science background, postgraduate qualifications to Ph.D., considerable experience in research and development, leadership skills, and a track record of innovation in the field.
What is the difference between CTO and Chief Science Officer?
While the CTO’s focus is more towards management and implementation of technology strategy within a company, in general, a CSO is usually responsible for scientific research and development. What does a CSO do in a biotech company?
What does a CSO do in a biotech company?
While responsible for supervising research and development in the invention of new biotechnical products, the CSO will have to make sure that such products will not infringe any regulatory standards. In addition, he or she will stimulate innovation and manage scientific teams as strategic drivers of success for their companies.

Conclusion
In all, the CSO’s role is instrumental in providing drive to innovation, compliance with regulatory affairs, and leadership for research and development within an organization. The strategic leadership of various corporate emphases-teams and stakeholder communication-all rest on the shoulders of the CSO as he shapes the future of the scientific enterprise at the company.
Whether one aims to become a CSO or be informed of the tasks that this senior role calls for, such insight is provided within the article as to what it takes to thrive in the position. Considering the ever-evolving scientific realm, the Chief Scientific Officer’s importance is, hence, bound to only gain more momentum and become an even more rewarding career choice.