Behavior Change Communication is considered to be an integral tool for the purpose of public health, social development, and corporate training. It intends to change individual and community behavior with an effective communication strategy. Most of the BCC programs do not bring about the desired outcomes. The conclusion of several researchers is that three quarters of the BCC programs do not achieve their goals. This blog post explains why these failures occur, the common pitfalls, and how to improve the success rate of BCC efforts.
Table of Contents

1. Understanding What Is Behavior Change Communication
Before going into the reasons for failure, it is important to have a clear understanding of what behavior changes communication and its importance in different fields.
What Is Behavior Change Communication?
Behavior change communication is the strategic application of communication to a positively desired behavior for health, proven and multi-channeled. Its message must be spread through mass media, community, and interpersonal communication as a means of facilitating information delivery, shaping attitudes, and bringing about behavioral changes.
This might be exemplified as follows: A BCC campaign to decrease smoking rates might use television commercials, social media campaigns, and community workshops so that the public can get educated about such dangers from smoking and its subsequent encouragement to join smoking cessation programs.
The Goal of Behavior Change Communication
The primary goal of BCC is KAP change, ensuring that the target audience learns and modifies their thoughts and behaviors for positive action. Such changes would help in addressing various public health issues related to HIV/AIDS prevention, maternal and child health, and vaccine uptake.
What is the purpose of SBCC? SBCC is a more generic term that brings together the BCC principles with social change approaches. SBCC can move beyond single behavioral change for the individual level to create a supportive environment for long-term behavior changes at both the community and societal levels.
What is BCC and what is SBCC?
The difference between BCC and SBCC- While BCC focuses mainly on individual behavior change, SBCC encompasses a much wider approach; that of social norms, culture, and structure in which behavior gets practiced. The application of SBCC is more holistic than that of BCC. SBCC does not limit itself to working just on individuals but rather uses the community mobilization process, policy advocacy, and capacity development for holistic policymaking.
2. Why Most BCC Fail End?
In spite of strategic planning and resources committed to BCC programs, most of the interventions fail to meet their objectives. It is important to explore these failures so that future BCC interventions are improved.
Lack of Formative Research and Audience Segmentation
One of the primary reasons BCC programs fail is because there is no formative research or proper segmentation of the target audience. Formative research is conducted to gather data about behaviors, beliefs, and attitudes of the target audience before a communication strategy is devised. Without this research, many BCC programs miss their target in catering to the unique needs and motivations of their audiences.
Example of Formative Research: A prelaunch formative research may discover that clean water is not easily accessible for many persons in the rural areas, thereby becoming a major issue to the behavior change. Otherwise, a BCC program will rely on information dissemination on how handwashing benefits many people, which may be wrong.
Poor Communication Strategies
Ineffective communication strategy is the other crucial factor contributing to the failure of BCC programs. BCC requires a systematic and strategic approach based on a combination of the right channels and the right messages designed to elicit the target audience’s response. An overreliance on mass media, without interpersonal communication or community involvement in the programs, normally fails to reach the audience.
Example: A vaccination campaign may use advertisements on TV to create awareness but not discuss local myths or misconceptions with the community through town hall forums, etc., as a result of which, such a campaign will barely reach the target audience.
Lack of Monitoring and Evaluation
Monitoring and evaluation are integral components of any successful BCC program. Ongoing monitoring provides the basis for assessing whether the communication strategy is working and thus determines areas that may require adjustments. Program evaluations at the tail end also contribute toward understanding the impact of the program and offering lessons that can be learned to contribute toward the success of future initiations. Most BCC programs fail to develop effective M&E frameworks and, hence, do not realize opportunities for improvement.
Monitoring and Evaluation Example: An anti-smoking program monitors the number of people attending anti-smoking workshops but cannot eventually evaluate change in attitudes or the rate of smoking over time, thus never being able to conclude the outcome of the program.
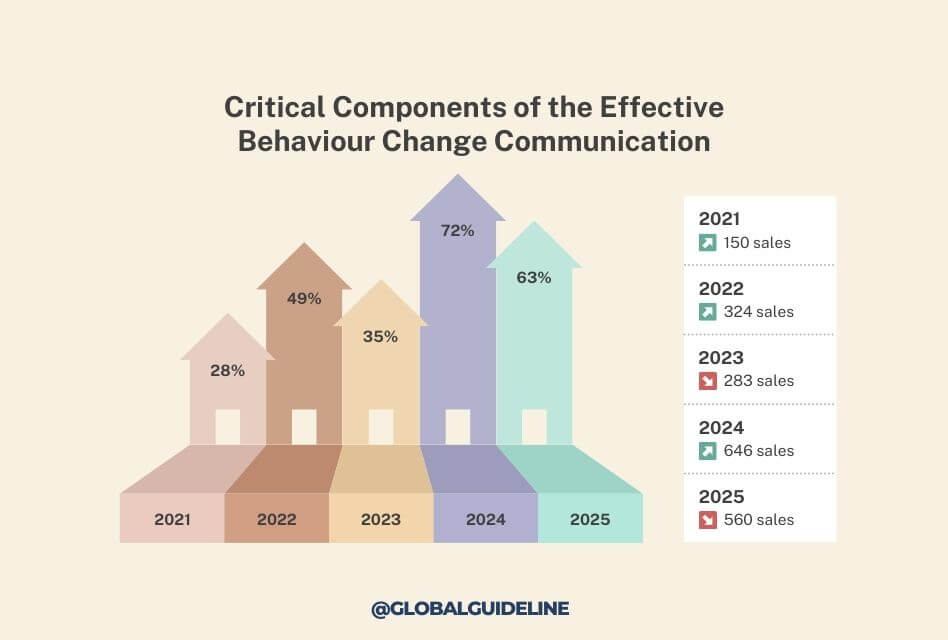
3. Critical Components of the Effective Behaviour Change Communication
A successful BCC program requires to know what elements are essential to effective behavior change communication, since a few minor changes can eventually boost the success rate of BCC programs.
Strategic Application of Communication Techniques
The most effective BCC programs make use of these approaches for communication as mass media, interpersonal communication, and community engagement, whereby the passage of the message through these channels will strategically reinforce the desired change of behavior.
This extends to social behavior change communication, which combines the above strategies with behavior change through changing social norms and overcoming structural barriers to desired behaviors.
Audience-Centered Design
The success of any BCC program is in the needs of its audience. That is, only when a person understands and takes on board the needs of current behavior, beliefs, and attitudes of the target group involved, such programming is designed and implemented through their involvement. The communication strategy designed for the target audience will remain relevant, culturally appropriate, and connected to the needs of the audience.
Audience segmentation would then take this form: A campaign to decrease teenage pregnancies would divide its audience according to age and sex and possibly by geographic location. Very different messages are then targeted for these various groups, depending upon their needs and concerns.
Ongoing Monitoring and Feedback
Continuous monitoring and feedback are actually crucial in the success of BCC programs. Monitoring the program’s progress from time to time should be done hand-in-glove with gathering feedback from the target audience and fine-tuning the communication strategy appropriately. This ensures that the program remains relevant and continues to be effective well into the future.
Example of a Feedback Loop: In the case of a breastfeeding promotion program, the collection of responses from mothers might be based on the results of surveys and focus groups, but then it would be possible to alter the messag-ing and support services based upon their feedback.
Integration into Broader Social Change Interventions
To ensure sustainable change of behavior, BCC efforts should be integrated into efforts toward other broader social change, including structural barriers like access to healthcare or education and working on changing social norms that affect behavior. Integrating these elements will ensure the impact of BCC programs goes beyond individual behavior change.
Social Change Integration Example: A domestic violence reduction campaign might include such things as change in law, services to survivors, women empowerment, and even communication strategies.
4. Successful Behaviour Change Communication Examples
Indeed, despite how difficult the problems are, there are many examples of successful BCC programs that made the difference. In fact, these programs could really be considered precious lessons in the design and implementation of effective BCC initiatives.
The “Truth” Anti-Tobacco Campaign
Among the most successful BCC programs is the United States’ “Truth” anti-tobacco campaign, initiated at the turn of the last century using the mix of mass and social media and community activities in order to reduce smoking among adolescents. Its success has been determined based on the customer-centered design, careful use of approaches to communication, and continuous monitoring and feedback.
The “Breakthrough ACTION” Program
Successful Examples of SBCC programs are based on USAID funded “Breakthrough ACTION”. Under this program, a country engages in health behavior change such as family planning, maternal and child health, and HIV prevention. A program has been observed to succeed through involving broader social change efforts, targeting audience-centered design, and strategic use of mass media and community engagement.
The “ABC” HIV Prevention Campaign
The “ABC” campaign to abstain, be faithful, and use condoms in Uganda is a notable example of a successful BCC program. Its success in reducing HIV infections can be largely attributed to the confluence of mass media, community engagement, and interpersonal communication for promoting safer sexual behaviors.
FAQ Section
Q: What is the meaning of SBCC?
A: SBCC is a program in which “Breakthrough ACTION” promotes health behaviors through a mix of mass media, community engagement, and policy advocacy.
Q: What are the words for behavioral change?
A: The definition of behavioral change is to alter the behavior of either an individual or a group by education or communication while sometimes policy is changed.
Q: What is the definition of SBCC process?
A: SBCC is a process of a series of steps that include formative research, audience segmentation, strategy development, implementation, monitoring, and evaluation. It mainly focuses on promoting sustainable behavior change.
Q: What are the different types of behavior change communications?
A: Mass campaigns, Community Engagement, Interpersonal Communication, Social Media Campaigns, and Advocacy for Policies
Q: What is the difference between BCC and SBCC?
A: BCC focuses on individual behavior change, while SBCC involves the broader social and structural influence that changes behavior, because it uses community mobilization, policy advocacy, and capacity building.
Conclusion
Behavior Change Communication is a very effective tool for promoting health outcomes and social change. Yet, its practice is also a highly complicated and challenging process because evidence indicates that BCC programs suffer from low success rates. With knowledge of the most common pitfalls in BCC and focus on some key areas, which include audience-centered design, strategic communication approaches, continuous monitoring, and integration into more global social change efforts, chances of success in these programs may be significantly enhanced.
For organizations and practitioners involved in BCC, it is more than that: a collaboration in defining who exactly the target audience should be, appropriate strategy steps for communication, and continuously review and change an intervention, which may help overcome challenges that have led many BCC programs to fail and thereby attain meaningful, lasting behaviour change.
Finding the right birthday wishes for a colleague is not a difficult task. You can use professional or sincere words, funny lines, or even a personalized message. What is essential here is that your birthday wishes be frank and represent your relationship with the person. Using examples and tips found in this blog post, you will certainly make your colleague’s birthday memorable and contribute to a positive workplace culture.
Remember, a thoughtful birthday wish can warm up the heart of anyone and strengthen professional relationships so take some time to come up with a best possible wish to make your colleague feel truly appreciated.
Related Posts:
Why 7 Out of 10 Fun Topics to Talk About Fall Flat in School?
How Chief Marketing Officer ThreatLocker Solves 3 Major Issues